![]() SEO, or search engine optimization, is a complex and constantly changing part of any website, blog, or online brand’s marketing success. In this guide, we will look at SEO from the ground up and describe the techniques and tools used to optimize web pages and entire websites. The goal is to rank higher in search engine results and receive a higher volume of organic, high-quality qualified, traffic. Acquiring this traffic that has already demonstrated an interest in the exact topic the page discusses, explains or the specific product being sold on the page is a primary benefit of SEO.
SEO, or search engine optimization, is a complex and constantly changing part of any website, blog, or online brand’s marketing success. In this guide, we will look at SEO from the ground up and describe the techniques and tools used to optimize web pages and entire websites. The goal is to rank higher in search engine results and receive a higher volume of organic, high-quality qualified, traffic. Acquiring this traffic that has already demonstrated an interest in the exact topic the page discusses, explains or the specific product being sold on the page is a primary benefit of SEO.
Most consumers (89%) now use search to guide their purchase decisions. This makes good SEO even more crucial to the success of e-commerce websites.
Start Out On a Solid Platform

The most popular website and blog platform is WordPress. WordPress allows you to utilize tried and true plugins and keep up with new technology developments easily. Because it is so widely used, support for WordPress sites is widely available. This platform excels on many levels and is built with SEO in mind.
Shopify and WooCommerce are two of the most popular e-commerce platforms. Both are excellent platforms, especially for SEO.
The Days of “If You Build It, They Will Come” Are Long Gone
Although SEO techniques are ever-changing and can be complex, the basic concepts of SEO are easy to understand. Even a little bit of knowledge can go a long way towards helping your web pages rank higher on search engines and receive more valuable, targeted search engine traffic.
The last thing you’d want is to put all the time and effort into building a great website that nobody who would be interested can find. That’s where SEO comes in.
In this guide, you will learn the best SEO practices and gain a foundation of knowledge that will give you the confidence to build and execute better ranking web pages and receive more targeted organic traffic.
“Organic” refers to search engine traffic a page receives through optimization, not purchased through ads. Organic web traffic is very valuable. Excellent SEO practices can easily garner more visitors than traffic gained through paid promotions.
SEO Starts With a Focus on User Experience
Making sure your content is unique, specific, and useful to visitors should always be the primary goal of content development and SEO. Focus on user experience is key, first and foremost. If you satisfy searchers with the information you provide, search engines will be more inclined to reward you with better rankings.
Search engines care about the quality of content and how well it serves the user before anything else. Before publishing web content always review it from a user’s perspective and decide if it meets the criteria of being user-friendly, informative, and/or entertaining, visually pleasing, and engaging. Would you recommend it to a friend or relative? Is it share-worthy?
When the content meets these all-important criteria, it can then be optimized to help search engine crawlers and manual reviewers recognize that it is a valuable piece of content and worthy of being recommended in top search engine results.
Major search engines have algorithms that analyze each web page cataloged. Search engines are successful when they deliver the best and most relevant content on the first page of search results. Google and other search engines are constantly striving to improve relevancy in search results. Your content must be extremely relevant to the keywords for which you wish to rank highly and must be exactly what searchers are looking for.
Key Ranking Indicators of High-Quality Content
Search engines send out crawlers that are constantly looking for the highest quality pages to recommend. Not only do search engines evaluate how relevant the content on the page is, but they also look at indicators of how popular the page already is across the web.
Great content that offers distinct value to users is often linked to from other reputable websites as a resource on the topic. When content gathers links from pages that search engines already find valuable, it gains credibility, is taken more seriously, and can rank much higher in SERPs.
Content that is widely shared on social media sites can also be an indicator to search engines that the content is useful and enjoyable and thus help boost rankings.
The Anatomy of Google SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages)
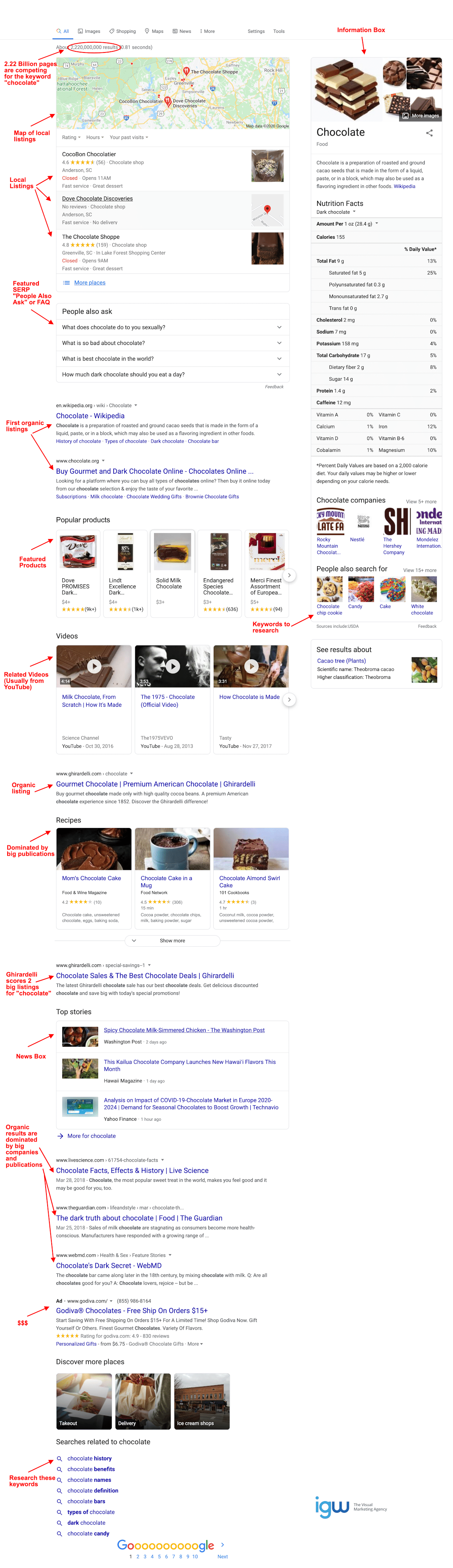
However, this situation is not hopeless.
There are also paid sponsored ads for chocolate vendors at the top. These top spots are purchased cannot be earned through SEO no matter how optimized your content is. Under the ad spots, you will usually see a clickable map of local places to buy chocolate and a SERP feature, which is a list of frequently asked questions on the topic.
The links to web pages appearing in the “People Also Ask” section are earned through SEO, which means your page could be featured here and is definitely something to strive to achieve. SERP features can give your web page a spot on the first page of seemingly impossible search terms.

Below all of these advertisements and links to standard chocolate informational pages comes the first place on the page for regular web pages to appear. Sprinkled in with these listings are links to purchase the most popular chocolate products, videos, news stories, and recipes.
As you can see, the search term “chocolate” only has a handful of regular organic listings for actual pages ranked by SEO on the first page of SERPs. This makes it nearly impossible for even most seasoned and talented SEO technicians to achieve a regular first page organic ranking for this term. However, you can see in the screenshot above, winning a featured spot can be done. In SEO, the strategy must be adjusted to fit each individual situation.
What Else Are Users Searching For?
What other words do people use when they search for chocolate? Are there other valuable related keywords with a high volume of searches but less competition, ie. fewer high-quality web pages dedicated to them to target instead? Good keyword research can answer these questions and give you priceless insight.
As you can see, there are some other great keywords to consider in the “searches related to chocolate” on the right side and at the bottom of the Google search results page.
Adjusting Your SEO Strategy for Best Results
Let’s look at how to find search terms that are doable and how to work around ones that aren’t. When researching keywords, you will be able to find search terms that have a high volume of traffic without being impossible to rank highly for on search engines. In other words, whether you are just starting out with SEO or are a seasoned pro, it pays to look for the low hanging fruit and compete for valuable search engine rankings on search terms without the stiff competition.
The amount of competition doesn’t mean that you can’t use SEO to help you sell chocolate online. It means that you will need to adjust your strategy and keyword optimize your pages in a way that demonstrates to search engines that your content is extremely valuable to searchers who are looking for chocolate. This is accomplished by using a wide variety of keywords and variations.
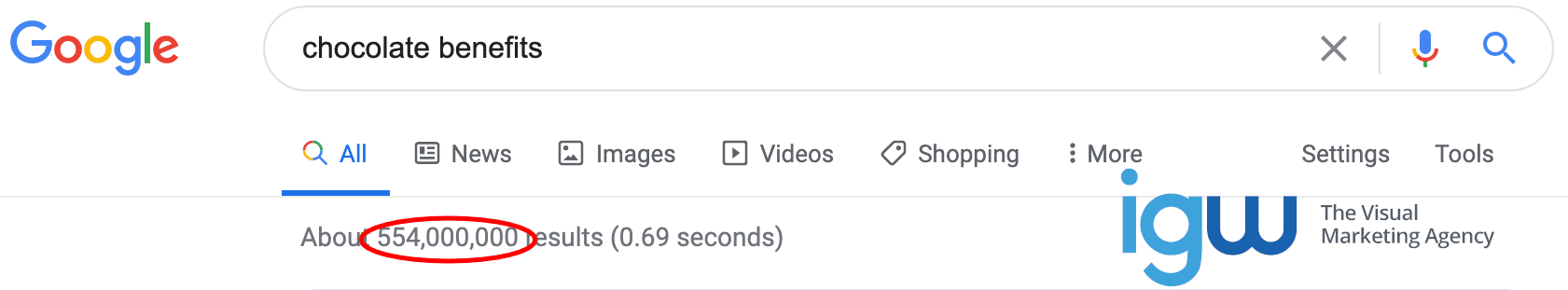
You can see that the competition for one of the terms shown in the “people also search for” section of Google search results is only 554 million, rather than 2.22 billion. Keyword research around the term “chocolate benefits” may uncover other keywords your page could rank well for without heavy competition.
Keyword Research
When planning your content strategy, keyword research will help you decide which keywords you should target and how to construct content to deliver highly sought-after information to users.
Keyword research will show you the search volume (how many searches a word gets per month) and help you better understand the needs of your target market and identify what words they search to try to find you.
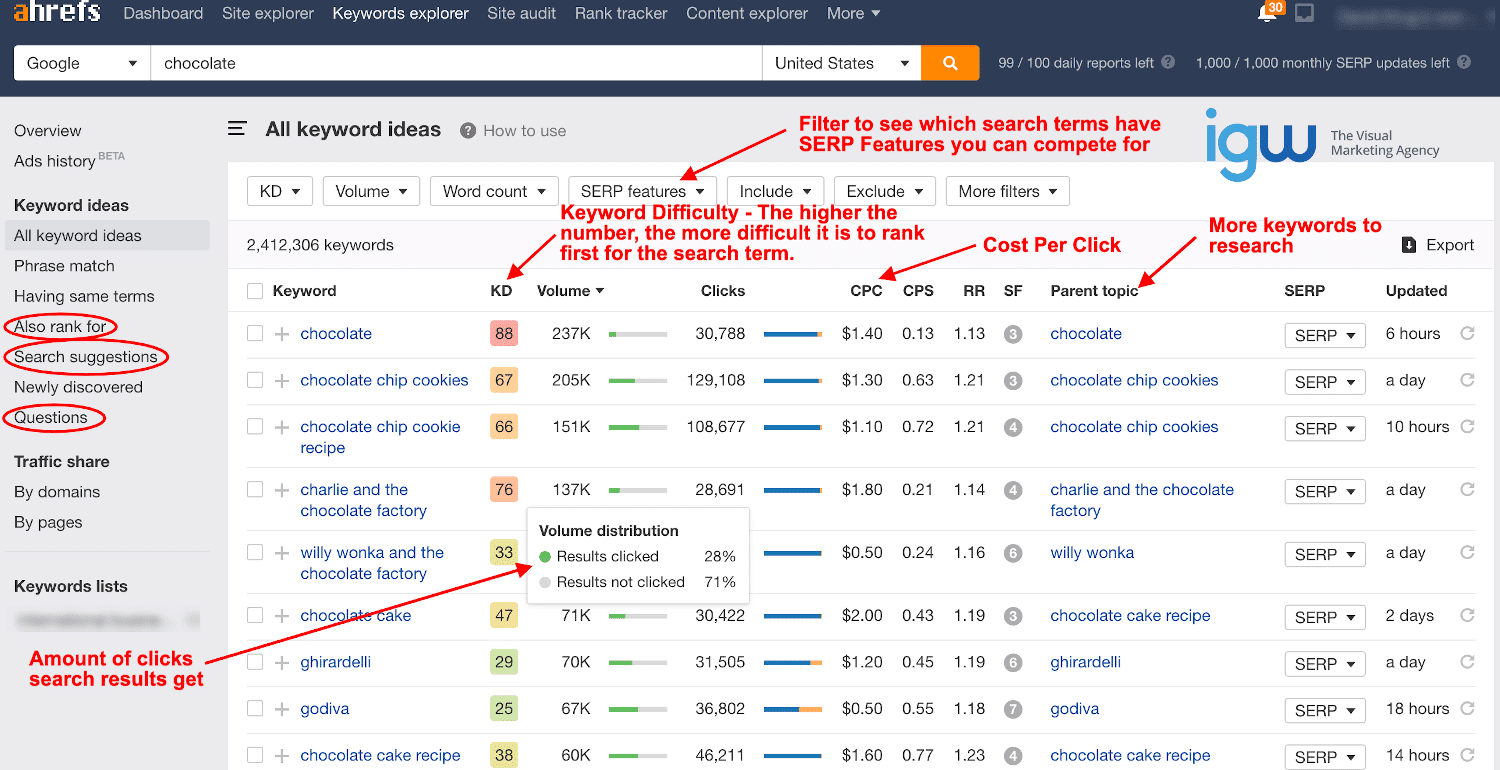
This is a screenshot of the keyword explorer at Ahrefs.com. Results can be filtered so that you can identify keywords related to your topic with low difficulty and high volume. You can refine results from each category on the left, with “Also rank for”, “search suggestions” and “questions” often turning up valuable keywords with SERP features you can win.
Ask the Right Questions
To determine where to start with keyword research you’ll first need to think like a reporter and ask all the who, what, why, when, and where questions about your target market.
- Who is searching?
- What keywords are they using in searches?
- Why are they looking?
- What is the searcher’s intent?
- When are the most searches made?
- Where are the users who are searching?
When you have the answers to those questions you can determine how to serve your audience best with high-quality content that connects with and satisfies searchers.
You can start by using a keyword research tool like Moz Keyword Explorer or Ahrefs to research your website’s core topics. Then branch out from there to find related keywords, common questions, and popular search variations.
How to Analyze Keywords
You’ll also find in your research that some relevant keywords may have a high volume (number of searches per month), but are also highly competitive. While you can’t compete for those keywords effectively right out of the gate (before your website is well established), you can find other similar keywords to target that have less search volume and less competition.
The highest volume keywords are more difficult to achieve a high ranking for because there is typically a lot of pages (and large companies) competing for those coveted page-one SERP rankings and SERP Features, like the “People Also Ask” example above.
When researching keywords for SEO you should also consider the CPC (Cost Per Click) of each keyword. This amount refers to the approximate cost per click if the traffic was purchased through Google adwords.
While you may never use adwords, the CPC can give you an idea of how valuable the traffic is and how well that traffic may convert into sales or leads. The higher the CPC of a keyword is, the better chance you have to convert clicks into sales.
Successful SEO is more about getting base hits and doubles consistently rather than trying to hit a home run every time. As your website grows and gains authority you will be able to build upon your success and target keywords with tougher competition.
Long-Tail Keywords
If your website is not established enough yet to rank for high volume, high competition keywords you can target long-tail keywords. A long-tail keyword is a very specific search term that typically has lower competition, thus making it easier for you to rank for. The best long-tail keywords also get a decent amount of searches per month as well.
Your keyword research should identify valuable long-tail keywords. A long-tail keyword can be valuable even if it has a relatively low search volume if it converts well. This means a higher percentage of users visiting your page from long-tail searches will buy a product, become a lead, sign up for your newsletter, or whatever your goal is on the page.
The more specific a keyword is, the easier it will be for you to deliver exactly what the user is expecting. Laser-focused long-tail keyword content can easily out-perform content optimized for large, broad terms.
Checking Out the Competition
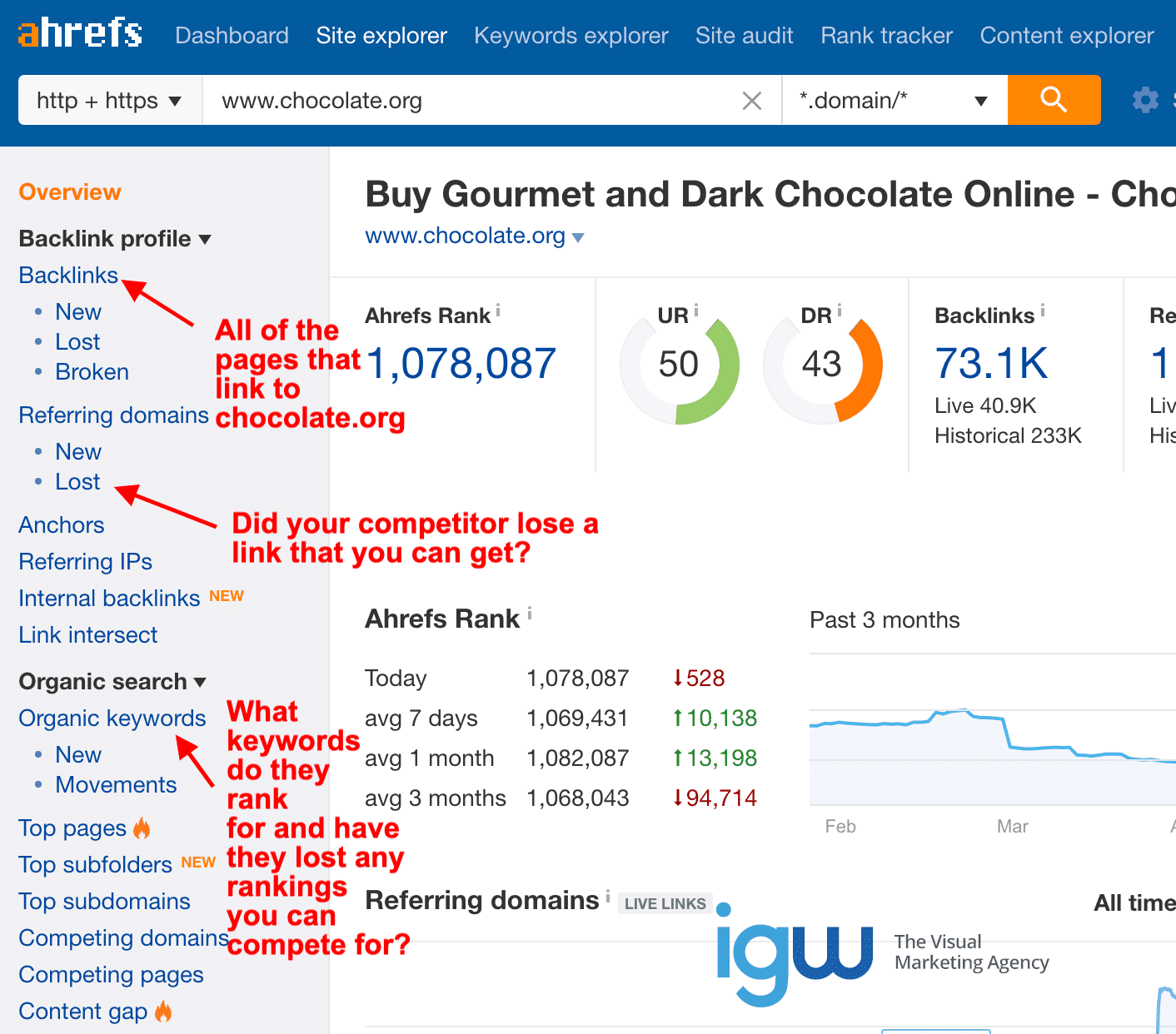
When you’ve identified a list of keywords you want to target, it’s a good idea to look into what keywords your competitors currently rank for and decide whether you’d like to compete for the same words or use keywords your competitors missed and don’t rank for already. If the field is wide open, why not? Your strategy may be a blend of both.
Ahrefs.com is an excellent tool to research competitors. It also allows you to conduct full site SEO audits to identify problems and offer valuable insights. It also allows you to do keyword research and filter results and is an all-around comprehensive SEO tool.
The Basics of Successful SEO
Be Accessible
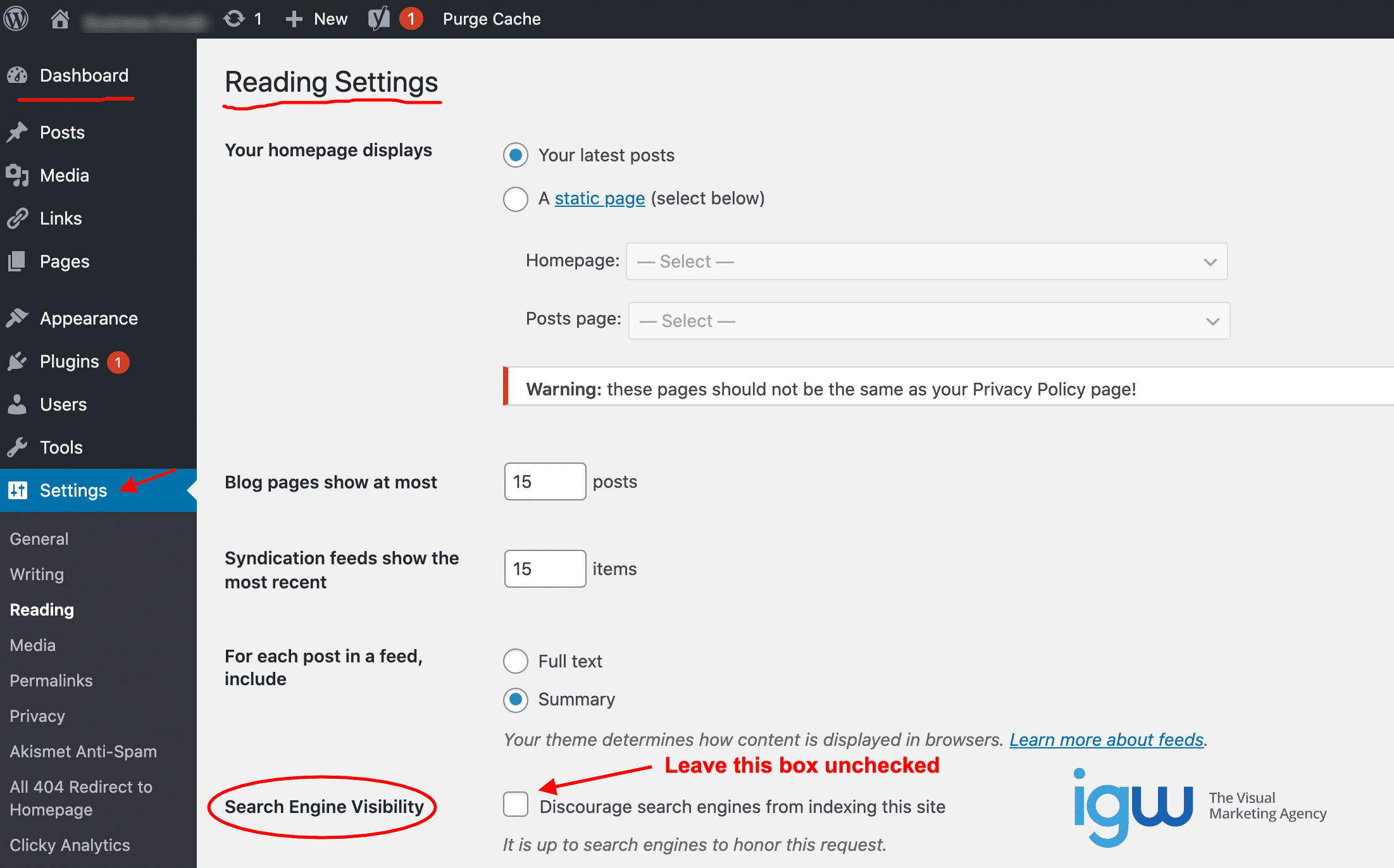
Before working to optimize a web page you must first make sure that your website settings are correct so that the search engine crawlers can reach the page and crawl through the content. The most perfect SEO practices will make no difference at all if the website and web pages you optimize cannot be accessed by search engine bots.
In the WordPress dashboard, choose “Settings”, then “Reading” and make sure the “Search Engine Visibility” box is not checked so that search engine spiders will be allowed to crawl the site.
Crawling, Indexing and Ranking
Search engine “spiders” or bots constantly follow links, crawl around the web, and gather information on billions of pages, PDFs, images, videos, and other web content. These spiders find new web pages and detect updates to already indexed pages. This action is called “crawling” and it is happening all the time.
A web page must be crawled by a search engine bot in order to be “indexed”, which means a cursory check determined the page is good enough to be added to the search engine’s catalog of web pages.
Once indexed, a page can appear in search results and this is where your SEO efforts have the opportunity to shine. How well a web page performs in the SERPs is what we call “ranking” which means where a page appears in the SERPs for specific keywords or how it “ranks” against other pages. Search engines rank results in order of relevancy with the best and most relevant content appearing on the first page of results.
Be the Expert on the Topic
When your settings are correct to allow search engines to visit your pages, you’ll then want to make sure your content is rich and compelling and focused to satisfy the searchers’ reason for searching. If a person searched for “Hawaii vacations” and landed on your page, that page should give them expertly organized, visually appealing informative content about vacationing in Hawaii with links to related content for more information, should they need it.
Optimize Content to Be the Best
After your richly informative content is prepared and published, the search engine optimization begins. You will edit your content to highlight important keywords and make sure the focus and purpose of the content are obvious to both users and search engines. Proper SEO helps major search engines recognize what your content is about, its purpose, and its overall value as an authority on the subject.
Black Hat and White Hat SEO
If you research SEO practices and techniques on the web, you’ll find that there are two schools of thought as to what is productive and effective.
-
Black Hat SEO
Black Hat SEO utilizes techniques that can be considered spammy or sneaky in order to try to outsmart search engine crawlers. Examples of these tactics are keyword stuffing, buying links, or otherwise artificially inflating the number of incoming links a page has and hiding links in pages. These techniques can work temporarily but come with a high risk of having entire websites permanently blacklisted by search engines.
Most Black Hat successes are short-lived, as search engines are already pretty smart and getting smarter every day. They also employ manual reviewers who are paid to look for these deceptive practices and prevent websites from profiting from them.
It’s best to avoid any Black Hat SEO techniques as you would any “get rich quick” scheme. The rewards are not worth the enormous risks. Once a website is blacklisted or penalized by a search engine there is no coming back from it, so it’s best to operate within the rules.
-
White Hat SEO
White Hat SEO utilizes techniques that are approved and recommended by search engines. The focus is on creating irresistible content that is well-optimized and appreciated by related websites. No sneaky business, no spamming or otherwise trying to skip the work, yet still reap the rewards. White Hat SEO is considered legitimate and above-board.
White Hat SEO is the type of SEO we focus on in this guide. Google is very much in favor of White Hat SEO techniques and has even constructed this beginner’s guide to SEO.
Advice From Google

Optimizing your content should only add to its value and provide the finishing touches to assist search engines in indexing the page.
According to Google, content creators should not publish useless content with little to no value to the user and avoid:
- Automatically generated or “spun” content
- Link gathering or trading schemes
- Hidden text and links (text and links in the same color as the page background or otherwise hide content from users)
- Cloaking (showing different content to the user than search engine crawler); and
- Doorway pages (dummy front pages optimized for specific keywords designed to funnel traffic elsewhere).
Why Care So Much About Google?
There are many search engines on the internet and they all have spiders constantly crawling the web and indexing content to serve up to searchers. Given that there are so many, why is there so much emphasis on SEO for Google? Why is a website completely ruined if it’s banned by Google and kicked out of its index?
The truth is that Google is king. It has the vast majority of the market share in searches. If you factor in all Google products such as Google Images, Google Maps, and Google-owned YouTube the company accounts for more than 90% of all web searches. This is why SEO experts focus primarily on Google.
Much of the same SEO guidelines for Google also apply to other search engines. While each has its own algorithms, they all operate in a similar way. Therefore if the content is optimized and performs well in Google searches, it can also perform well on other search engines, the rewards are just much smaller.
Choose a Fast and Reliable Web Hosting Company
You’ll also need to make sure your web server delivers your content quickly and without errors to all users and search engine bots. The load time of a page is part of the search engines’ criteria when weighing out which pages rank the highest.
Share Your Content with the World

In order to get your content out to an audience who will appreciate it, you will reach out to other related websites that are not your direct competition to see if they may like your content enough to link it and share it with their audience.
If your content gathers no links or social shares, it’s time to re-evaluate your content to see how you can improve it and make it more valuable so that it will naturally gain links, social shares, and other recommendations on the internet.
Give Search Engines the Best Summary of Your Content
To make sure your content shows up as intended in search engine results, you will need to craft a clear and compelling title and succinct, relevant description of the content and make sure these optimized values are what the search engines and searchers see. This will improve your SEO results.
The URL of your content should also be chosen to logically include the keywords for which the page is optimized.
Stand Out and Be Featured in SERP Features
In order to really stand out to search engines, you can also add specific featured snippet/schema markup within your content. Featured snippet markup allows content on a web page, such as FAQs, images, ect., to be highlighted within the SERPs so that it really stands out and can bring much more traffic.
Search engines are adding more SERP features all the time and while some are paid sponsorships or landmark data sources, some are organic, which means your quality content can be featured and highlighted in search results.
Local SEO
If the website you are optimizing operates face-to-face selling or providing a service within a particular locality or has a brick and mortar storefront, it qualifies for a “Google My Business” listing.
To be included in the Google My Business index the business must have a physical location, even if it is a home address and be open for business.
When setting up a Google My Business listing, be sure to provide accurate information about the business, including its legal name, physical and web address, phone number, business hours, the correct category of the business, and other features it offers.
By all means, read Google’s guidelines and avoid creating Google My Business listings for businesses that do not meet the basic criteria. Also, avoid making any misrepresentations about the business and be sure to provide a real physical address rather than a P.O. box. Do not solicit fake reviews of your business or attempt to hurt the competition by leaving unfavorable reviews.
Good SEO Considers User Intent and Fulfills the Need
What words did the user search for? Are you providing what they are looking for?
Getting lots of organic traffic can be great, but only if users find what they were looking for when they click to visit your web page. The “bounce rate” listed in your website metrics give you the percentage of users who visit your page and quickly leave. A high bounce rate means your page is not engaging and visitors are not finding it to be of any use to them. This means the content needs to be upgraded to provide a better user experience.
Optimize SEO Strategy to Meet Specific Goals
What are the end goals of the web page you are doing SEO work on? Obviously you are working to improve search engine rankings and ultimately bring a greater volume of qualified traffic to the website, but traffic alone doesn’t equal profits.
The traffic a web page receives is part of a bigger goal, to make a website more profitable. Keep your eye on the bottom line and make sure the organic search traffic your page receives is useful to your ultimate goals, whether that is capturing leads, selling products, or showcasing affiliate links.
Establish Goals, Plan For, and Measure Success
How will you measure the return on SEO investment?
Consider what benefits you intend to get from an increase in organic traffic. For example, if your business model depends on capturing leads, look at the ratio of visitors to leads to determine how effective your page is. This ratio is called the conversion rate. If traffic increases but leads don’t, this is an indication that your page needs more work to convert better.
Likewise, if you are working with an eCommerce site, an increase in organic traffic should yield more sales.
You should install Clicky Analytics or other metrics package to gauge your success and give you insight into how your website is performing.

Check That Google Has Indexed Your Pages
An easy way to make sure that Google has indexed your web pages is to go to Google.com and type “site:yourdomain.com” in the search bar, without the quotes and, of course, substitute your domain name in place of “yourdomain.com.” This search will show the indexed pages of your domain in the search results. From there you can see how many pages of the site appear in Google’s index and how the listings are displayed.
Use Google Search Console
Another way to check on your site health according to Google is to monitor your results in Google Search Console. You can sign up for a free account here. Google Search Console will allow you to submit sitemaps for your site, see how often it is crawled, which pages are indexed, add rich snippet tags, and keep an eye on how Google views your site overall.
Your sitemap should not include pages that shouldn’t be indexed. Not every page of your website should be crawled by search engine spiders. We’ll discuss this more later.
When To Use a 301 Redirect

If a page on your site has moved to a new URL, rather than having the old URL return a 404-not found error, you will need to implement a 301 redirect.
A 301 redirect allows search engines to recognize the content has permanently moved to a new location and transfer the earned merits of the old URL to the new location of the content.
Users who follow a link to the old URL are automatically taken to the new URL so that the content doesn’t lose its link equity, search engine rankings, confuse search engine spiders or provide a frustrating user experience.
If your website platform is WordPress (and we’re not sure why it wouldn’t be) you can install a plugin to allow you to implement 301 redirects. Be cautious with redirects and don’t implement a 301 redirect, then later implement another redirect on the new URL. A good rule of thumb is to craft URLs in such a way so that you rarely have to use redirects.
If Your Site Is Not Indexed by Google
If you have searched Google and use the Google Search Console and do not see any pages of your website indexed, it’s worth looking into the possible reasons before continuing your SEO work.
When a website is brand new, Google must find it by following a link on an already indexed site. And in order to crawl your entire website and index all of the pages you want it to, the website’s navigation must be easy for the spiders to crawl.
Implement Great Site Navigation
If your site’s navigation is confusing and difficult to follow there is a risk of some important pages being excluded from search engine indexing. Bad navigation also provides a bad user experience. If search engine crawlers can’t find the content, there is little chance users will either.
A good rule of thumb is that no page of a website should take more than two clicks to reach. This means that content must be cleanly organized into categories that are visible and easy to navigate. Provide helpful internal links within your content to related pages on your website.
If a website has at least one link from an already indexed external site and the navigation is easy (or should be easy) for search engine spiders to follow yet it is not being indexed, make sure your website doesn’t contain any code to block crawlers from content you want to be indexed.
No Logins Required
If your content requires a login, search engine crawlers cannot log in and access it, so it would not be indexed. From your homepage, crawlers should be able to follow internal links to discover all of the content you expect to be indexed.
No Orphaned Content
If any of your pages are “orphaned” (not linked to from any other page on the site and not included in the navigation) the search engine spiders will not be able to find it and it won’t be indexed. It might as well not exist.
Good website structure allows users and crawlers to efficiently move throughout the site. Organize your content so that it flows and is intuitive, which makes it simple for all of your content to be found by people and search engines. You may also want to include a sitemap and submit it from within Google Search Console for more complete coverage by crawlers.
Worst-Case Scenario – Game Over
The worst-case scenario is that the website is not being indexed by Google because it is banned or penalized for Black Hat SEO tactics. In Google Search Console you can check for penalties and communicate with Google on a limited basis, but when a domain is blacklisted by Google there is little to no chance of reversal of this decision, even if the website has changed owners.
How to Exclude Some Pages from Indexing
With Google spiders, you want to always put your best foot forward and make sure the crawlers make note of all of your best work. However, most websites have some pages or sections that do not need to be indexed by search engines.
Any content that is weak, thin or not the best quality should be excluded from crawlers. Duplicate content, staging, and test pages should also be excluded. This is especially important for very large sites as a Google crawler will only crawl for so long before it leaves your site and you want to make sure it gets the good stuff while it’s there. To exclude some pages from search engine crawlers you can use a file called robots.txt in the root directory of the website.
Google crawlers always look for a robots.txt file on every site before crawling. A robots.txt file is used to suggest to search engines which parts of the website it should and should not crawl and at what frequency it should re-crawl to look for updates.
Larger websites that post new content often are crawled more often than smaller blogs.
Search engine crawlers typically follow the suggestions found in the robots.txt file if it exists. If there is no robots.txt file the crawlers will attempt to crawl the entire site. If there is an error while Google crawlers attempt to access the robots.txt file the crawl will be skipped.
SEO for e-Commerce
With care and attention to these specific e-commerce ranking factors, your e-commerce store will rank better on Google. Many of these ranking factors apply to all websites but are of particular importance to SEO for e-commerce websites.
These factors include:
- Use of Own Domain Name
Register your own domain name for your business. Search engines won’t take you seriously without a dedicated domain name for your brand. Your domain name will also make it easier for customers to find and remember you. - Navigation Links
Navigation links are the text links to categories or products in your e-commerce store’s menu. Most e-commerce platforms offer independent control of navigation links. Navigation links should be concise and descriptive on all websites. - Page Titles
Page titles on all websites and especially e-commerce sites should contain the target keyword of the page, preferably at the beginning of the title. It’s to your advantage to edit the titles manually especially if your e-commerce platform automatically generates page titles. - Integrated Blogging Platform
Your e-commerce store should include a blog. The blog content can be optimized much more efficiently than individual product pages. - Page URLs
Short, descriptive, pretty URLs win rankings for any website. Make sure your e-commerce platform allows you to assign your pages custom URLs. - Meta Descriptions
The meta description of a page appears under the URL on SERPs. The description should be engaging and designed to draw clicks. This is also true for all websites, but especially important for e-commerce websites. If you don’t specify a description for a page, Google will typically choose the first text on the page as the description, which is not optimal for SEO. - Auto XML Sitemaps
Your e-commerce website platform should automatically create an XML sitemap. If it doesn’t, install an XML sitemap plugin to create one. - Social Sharing Buttons
It’s especially important for e-commerce sites to include social sharing buttons on all pages of the website. - Canonical URLs
If the content on your e-commerce store can be accessed by more than one url or if there are similar versions of the same content on your website, Google views this as a duplicate content issue and will only choose one version of the page as the real deal, or the canonical version. Duplicate content urls won’t be crawled as often and are less important to Google.Google recommends that you specify a canonical url for each unique page of your e-commerce website. You can find these recommendations here. - Image ALT Tags
Adding ALT tags to images is a good SEO practice for all sites, but for e-commerce stores, it can be even more important. ALT tags should be a brief description of the product using key search terms. Adding ALT tags to your images can improve the chances of the image appearing in Google’s image search results, which can bring more traffic to your business. - H1 Headings
The H1 tag is typically the title or main heading of a page. On e-commerce websites, you should be sure your platform allows you to manually edit H1 tags. - Your Own IP Address
In addition to registering your own domain name, your e-commerce website should also have its own IP address. Your hosting company should provide this service for a fee. - 301 Redirects
If a page on your e-commerce website has moved, you will need to implement a 301 redirect to make sure users and search engines can still find the page, even if they follow an old link. - Robots Noindex Capabilities
Your e-commerce website must have the capacity to instruct search engines to exclude certain parts of your website. This is used to avoid search engines from crawling duplicate content with different dynamic URLs.
How To Manage Duplicate URLs on e-Commerce Websites
Most e-commerce websites have search parameters set up within the web store to help shoppers easily narrow down selections and find what they need. Each refinement typically appends the URL with identifiers. While searching for a size 7 women’s sandal on a shoe website, it is easy to narrow down the selections. However, it can make for some long, ugly, duplicate URLs being indexed.
In Google Search Console you can let Google know exactly how you would like for them to index your content. This means you can let the pages be indexed with short, descriptive, tidy URLs and instruct the crawlers not to index dynamic URLs with parameters. It’s a good idea for e-commerce sites to do this to avoid duplicate pages being crawled and indexed.
What Is Indexing?
When search engine spiders crawl a web page they take a snapshot of the page, look at it as a web browser would, and analyze the content. This snapshot and analysis are stored in the search engine’s index. The index provides search engine results.
Robots Meta Tags
You can provide directions (schema) for search engines on how to index your page. The most simple way to do this is to add robot meta tags with instructions to the page. Meta tags appear in between the <head> and </head> tags of a website.
Types of Robots Meta Tags
For example, using “noindex” in the robot meta tags lets crawlers know the page should not be indexed. Using “noindex” doesn’t hide content from users.
Using “nofollow” in the robot meta tags of a web page directs search engine crawlers not to follow and crawl the links on a page.
Using “noarchive” in a web page’s robot meta tags tells the search engine crawlers not to save a cached copy of the page. This tag is often helpful to e-commerce websites that run sales or change inventory frequently to prevent out-of-date prices or unavailable products being shown.
Can Pages Be Removed From the Index?
Web pages can be removed from the index if the URL returns a 404 error or a server error prevents the content from being crawled. The content can be re-indexed if it returns.
Sometimes a page that should have been excluded from crawlers accidentally gets indexed or you may find that you want to have a page removed from the index for another reason. In this case, you can add a “noindex” robots meta tag to the page to let search engine crawlers know it should drop the page from the index.
Some web pages are removed from the index because the URL becomes password protected. Since spiders can’t log in to crawl, the page is considered gone.
Again, the worst-case scenario for a web page is to be dropped from the index because it has violated webmaster guidelines. This is typically a manually applied penalty that is permanent. The web page will not be re-indexed and the search engine’s spiders will no longer crawl the website. If you suspect your website has received a manual penalty and dropped from Google’s index, log in to Google Search Console and check.
How Search Engines Rank Pages
As we’ve mentioned earlier, search engines use complex and ever-changing algorithms to determine how pages rank for specific keywords based on relevancy.
Google makes small changes to its algorithms every day. Most days are small tweaks and improvements, while other updates have been designed to combat Black Hat SEO practices.
Owners of websites that suffer a steep decline in rankings after Google algorithm updates are encouraged to review Google’s Quality Guidelines and make the necessary adjustments.
The Importance of Links in SEO
For the purposes of this SEO discussion, there are two types of links. Here we will explain what “backlinks” or “inbound links” are and how they are different from “internal links.”
A Backlink or Inbound link is a link to your website from another website. The more established, trustworthy, and authoritative the search engines view the website that links to your site, the more valuable that link is to your website. Search engines look at the contextual relevance and quality of inbound links a website has earned to help determine its value and where it will rank.
We mentioned internal links briefly when we discussed good website navigation. Internal links are links on your web pages that point to other relevant content on your website.
How to Optimize Website Content
While keeping in mind that user experience is of primary importance, web content can be structured, edited, and optimized to line up with what search engine users are searching for. Not only does the content need to have the exact words the user typed into the search engine, but it also has to fulfill the expectations the user had when making the search.
Use Header <Hx> Tags for Structure, Organization, and Emphasis
The more thorough, well-organized, and informative your content is, the easier it will be for users to find the answer to the question that prompted the search. Using <H2>, <H3>, and <h4> tags within your content helps set up the structure of your content.
SEO Mistakes to Avoid
To achieve high search engine rankings for particular keywords, content should be centered around those words and phrases, but this does not mean to use them over and over again in your content.
Search engines are intelligent and have vastly improved the quality and accuracy of search results in recent years. Repeated unnecessary and unnatural use of keywords and phrases diminishes the user experience. This technique is considered spammy and can hurt your website’s rankings in search results.
Avoid Black Hat SEO Tactics
Because your content is full of substance and value to the user there is no need to attempt to trick search engines into ranking you higher (and you shouldn’t do that anyway). In recent years search engines have developed an advanced understanding of language, context, and semantics.
If your content is well-focused and the best resource on a topic it will naturally gain valuable links from other websites, be shared on social media, and consistently outrank thinner lower-quality content.
SEO for Videos and Images
Although having videos and images in your content can make it more interesting and informative and is recommended, these components must be optimized to improve your SEO.
When your web page contains non-text content, such as images and videos, any text that appears on that content won’t be crawled by search engine spiders. You should add descriptive alt text and/or captions to images that spiders will read as part of the content.
How Google Gauges Search Performance
There are many ranking signals Google measures that can cause a rise or decline in a page’s ranking. Ranking adjustments are constantly being made as a result of user behaviors.
As you may have noticed, the central theme of this guide is the importance of creating extremely high-quality content that satisfies users’ intent. There are several ways Google measures click data to evaluate a web page’s quality and ranking performance.
The number of clicks your page gets from the SERPs matters. The title and description of your page should be crafted to be succinct and appealing and include your main keyword or phrase. Your page could drop in rankings if it doesn’t attract users and get as many clicks as pages ranked below it. On the other hand, if your title and description attract many more clicks than higher-ranked pages, you could gain rank.
It also matters how long users spend on your page, whether they visit more than one page on your site or if they click to visit your page and immediately return to search results to choose another page.
Google is always working to improve user experience, so click data provides valuable insight into which pages deliver the best results for the search.
How to Get Featured By Google
You may have noticed that Google search results are constantly evolving with new features rolling out all the time. And also, there are a lot more ads.
These features on search result pages are called SERP features. While many of the top spots for highly competitive keywords do go to companies that pay top dollar for them, other features allow top organic content to also be featured.
Some organic SERP features include featured snippets, image packs, local packs, news boxes, related questions, reviews, site links, and videos.
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are excerpts of pages that answer a user’s query. They receive more clicks than regular organic results. Typically featured snippets are extracted from a page that already ranks in the top 5 organic results.
This year Google announced that featured snippets would count as one of the ten web page listings shown on a SERP. Previously, the site elevated to the featured position (also called “Position 0”) would also retain a spot in the top organic results. While the featured snippet position is still important, its reward isn’t as large as it used to be.
- Local Packs and Local Teaser Packs
Local packs appear on keywords Google thinks have local intent. This SERP feature displays three physical locations assumed most relevant to the search.
Another version of this SERP feature is the local teaser pack. This displays three local business results, which are usually hotels, restaurants, or major attractions, with hours of operation, reviews, and images with the option to sort by price or rating.
- News Blocks
Breaking news and current event content can appear in a block of results from Google News. To appear in this SERP Feature a web page must appear on Google News. Although not required, signing up for the Publisher Center is recommended and offers several advantages.
- Related Questions
The related questions feature shows questions the Google algorithm believes are related to the search. Related questions expand with a featured snippet answer extracted from a web page and a link to that web page.
Usually, the listing that earns the featured snippets position on the SERP is also featured in related questions.
- Reviews
The reviews SERP feature appears on searches related to products, hotels, restaurants, recipes, and any other business that receives a rating. Earning this feature really draws the eye and can increase clicks.
- Site Links
When a user searches for a specific website by its exact domain name, the SERP may display up to 10 links to different pages or sections of the website.
- Videos
Google SERPs often display video results for certain searches. The videos featured are typically YouTube videos. Video SERP features were larger in the past, but are now a listing with a video thumbnail included.
Structuring Content to Compete for Featured SERPs
Use schema markup to make your pages easier for Google to understand and get you a step closer to a featured SERP listing. This means adding structured data (also called rich snippets) to pages in the language easiest to digest by Google. Schema helps direct Google and other major search engines specifically to the most important parts of a page. Pages that rank well and also have rich snippets are more likely to win the featured spots.
Including structured data in custom HTML tags within the page’s <head> can help it rank better on Google and make it easier for Google to promote the page to a featured spot on SERPs.
If your website platform is WordPress, you may already be adding some structured data to your pages. SEO plugins like Yoast SEO Plugin and All in One Schema Rich Snippets Plugin insert schema markup dynamically into your pages according to the information you specify on each post or page, such as title and description.
To get started creating the custom rich snippet markup for your pages you can use a generator like this one to create several types of rich snippets, depending on the content type.
For an easy to use FAQ Page rich snippet generator this tool is also handy. Including FAQ rich snippets is a great way to win the “People Also Ask” SERP feature.
As a rule, use “snippets” of content directly from your page to construct your rich snippets. Don’t include content in your rich snippets that users can’t easily find on the page.
You can test your schema markup here.
Deploying Structured Data Markup
Custom schema markup in the JSON-LD format can be executed in the <head> of the page if you are not using an SEO plugin that automatically inserts data markup into the page.
After you generate and test the structured data tags, you will deploy the code on your page in one of three ways.
1. You can use a plugin that allows you to insert the custom code into the headers of specific pages. Here is an example of a plugin that accomplishes that for you: Header and Footer Scripts WP Plugin by Digital Liberation.
2. You can also use Google Tag Manager to add structured data dynamically, without editing your website’s code. The downside to this method is that other search engines won’t be able to gather the data you provide to Google. Hallaminternet published a great guide on how to add your schema markup using Google Tag Manager here.
3. The third way to deploy the structured data tags is by editing the functions.php file in your WordPress theme by pasting the code at the end of the file and saving the changes. It’s a very simple edit, but if this way makes you nervous it’s best to use one of the previous two options.
Wrap Up and Review:
10 Things to Remember About SEO
A standard component of the “for Dummies” series of books is the “tens” section at the end where the author highlights and reviews ten important concepts that were covered in the book. While you’re far from a dummy if you’ve followed this SEO guide, we’d like to wrap it up in a similar way to give you a summary of the best SEO practices we’ve covered for quick reference.
1. Provide Superior User-Focused Content
If you don’t already know that the first and foremost concern of SEO is the importance of providing a topically focused, high-quality user experience on your website, you either haven’t read this guide or we have totally failed you. We’re betting on the former.
Be the best to get the best search engine rankings.
2. Select a Reputable Web Hosting Company
Your quality website must be fast and reliable. Choose a web hosting company that you are confident can provide great service. Web server errors and slow load times can hurt your rankings.
It’s a wise investment to pay what you need to in order to put your website in good hands.
3. Be Accessible to Search Engine Crawlers
Make sure search engine crawlers aren’t blocked from crawling pages that should be indexed. By the same token, use robots.txt or a “noindex” tag to exclude certain pages from indexing. Use 301 redirects to let search engines know a page has moved.
4. Ensure Intuitive Navigation
Your website structure should be organized in a way that is easy and natural for users and search engine spiders to navigate. Use internal links to relevant related content in your web pages.
5. Research Keywords
Spend a lot of time getting to know your audience through researching keyword data. Fulfill searchers’ needs with your content by knowing exactly what words are most commonly searched.
Craft answers the most asked questions and provides easy to find information based on specific keywords related to your website’s topic. Your research and interpretation of search data will determine which exact keywords and phrases you should target to achieve the best SEO results.
6. Optimize Content
Diversify your content so that each page is optimized to rank for unique and valuable keywords and phrases. Make sure your pages clearly deliver what searchers expect.
7. Add Structured Data/Rich Snippets to Web Pages
Schema is the language that search engines understand best. By adding structured data (rich snippets) schema markup to your web pages using robots meta tags you can improve your rankings and have the opportunity to win a featured spot on Google SERPs.
8. Establish Authority
Research your competitors to discover which types of sites are linking to their content. If your content is better, these sites may want to link to you instead. Introduce your page to websites that are known to reward great content similar to yours with inbound links.
9. Measure SEO Success
Regularly review your progress and assess the goals you’ve reached, then set higher goals. Also, review content that has not performed well for you and determine how to improve it to better fulfill searchers’ intent.
10. Experiment, Tweak and Improve SEO
As SEO is a constantly evolving field, you’ll want to read what Google has to say on its webmaster’s blog and experiment with new SEO techniques to improve your rankings. Ranking highly for search terms is not a “one and done” thing, to maintain high rankings you have to stave off competitors and continue to be the best Google can offer searchers. Once your business website is driving traffic and leads, finding the best managed SEO services for your business will help you reach the next level, whether it’s for keyword research, general SEO strategy, on page SEO services, or anything in between.
SEO Tools and Resources
SEO Tools
WordPress
Shopify
WooCommerce
Moz Keyword Explorer
WordPress SEO Plugin by Yoast
All in One Schema Rich Snippets Plugin
Redirection WP Plugin
SEMrush
Ahrefs
Answer the Public
Header and Footer Scripts WP Plugin by Digital Liberation
Schema Markup Generator
FAQ Rich Snippet Generator
Clicky Web Analytics
SEO Resources
Google Webmaster Help Center
Ecommerce SEO: A Simple (But Complete) Guide
ECOMMERCE SEO: The Definitive Guide
Add Schema Markup to Site with Tag Manager